6.2 HashSet和TreeSet

系列 - JAVA集合
目录
本节摘要
这一节我们将学习Java中三种重要的Set集合:HashSet、LinkedHashSet和TreeSet。通过动手实验,你将掌握它们的基本使用方法、去重特性以及排序功能。特别是TreeSet的自动排序功能,能让数据按照指定规则有序存储。
任务一:HashSet的基本使用
HashSet是Java中最常用的集合之一,它最大的特点是不允许重复元素。让我们从简单的例子开始学习。
Step 1 存储基本类型
下面的代码演示了HashSet如何自动去除重复元素:
import java.util.HashSet;
public class Example08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<String> names = new HashSet<>();
names.add("张三");
names.add("李四");
names.add("王五");
names.add("李四");
System.out.println(names);
}
}
观察结果
运行上面的代码,注意观察输出结果。虽然我们添加了两次"李四",但HashSet会自动去除重复,最终只保留一个。
Step 2 存储自定义类型
当我们要在HashSet中存储自定义的对象时,情况会有所不同。让我们看一个例子:
import java.util.HashSet;
class Student {
String id;
String name;
public Student(String id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public String toString() {
return id + ":" + name;
}
}
public class Example08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<Student> students = new HashSet<>();
Student s1 = new Student("1", "张三");
Student s2 = new Student("2", "李四");
Student s3 = new Student("2", "李四");
Student s4 = new Student("3", "王五");
students.add(s1);
students.add(s2);
students.add(s3);
students.add(s4);
System.out.println(students);
}
}
问题出现了
运行上面的代码,你会发现输出了4个学生,包括两个相同的"2:李四"。这是因为HashSet判断两个对象是否相同时,需要用到
hashCode()和equals()方法。要解决这个问题,我们需要在Student类中重写这两个方法:
修改后的代码:
import java.util.HashSet;
class Student {
String id;
String name;
public Student(String id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public String toString() {
return id + ":" + name;
}
public int hashCode() {
return id.hashCode();
}
// 判断自己和obj是不是相等
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
// 如果obj就是自己
if (this == obj) {
return true;
}
// 如果 obj 不是 Student 类型
if (!(obj instanceof Student)) {
return false;
}
// 把 obj 转换成 Student(强制类型转换)
Student other = (Student) obj;
// 我们认为学号相等就是同一个学生
return this.id.equals(other.id);
}
}
public class Example08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<Student> students = new HashSet<>();
Student s1 = new Student("1", "张三");
Student s2 = new Student("2", "李四");
Student s3 = new Student("2", "李四"); // 和s2学号相同
Student s4 = new Student("3", "王五");
students.add(s1);
students.add(s2);
students.add(s3); // 这个不会被添加,因为学号重复了
students.add(s4);
System.out.println(students);
}
}运行结果:
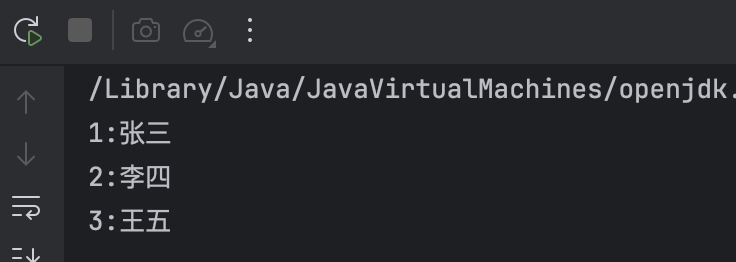
现在正常了
重写了
hashCode()和equals()方法后,HashSet就能正确识别重复的学生了。现在输出结果只会显示3个不同的学生。任务二:LinkedHashSet保持插入顺序
HashSet的一个特点是不保证元素的顺序,但有时候我们希望保持插入时的顺序,这时可以使用LinkedHashSet。
动手试试
把刚才代码中的 HashSet 改成 LinkedHashSet,观察输出顺序的变化:
LinkedHashSet<Student> students = new LinkedHashSet<>();任务三:TreeSet的自动排序功能
TreeSet最强大的功能是自动排序。它会把存入的元素按照一定规则自动排列。
Step 1 观察自动排序
让我们先看看TreeSet如何对数字进行排序:
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class Example11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet ts = new TreeSet();
ts.add(3);
ts.add(1);
ts.add(1);
ts.add(2);
ts.add(3);
System.out.println(ts);
}
}运行结果:
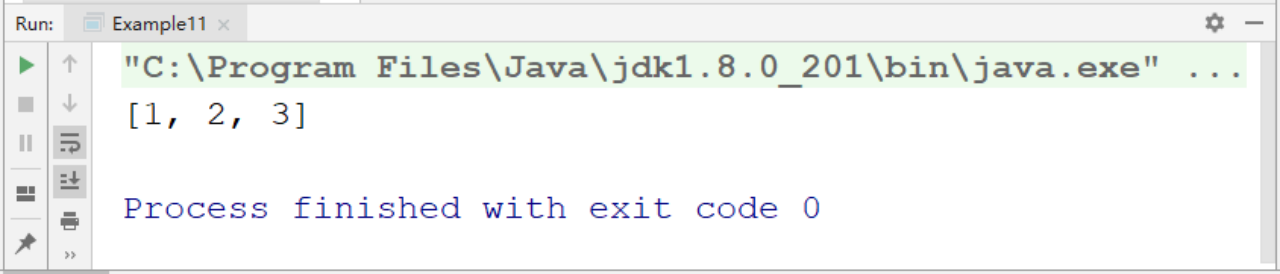
自动排序
可以看到,尽管我们是按3、1、1、2、3的顺序添加的,但TreeSet自动按照1、2、3的顺序排列,并且去除了重复元素。
Step 2 存储自定义类型
当我们想让TreeSet存储自定义对象时,需要告诉它按照什么规则排序:
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class Example12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student("1", "张三");
s1.setHeight(175);
Student s2 = new Student("2", "李四");
s2.setHeight(170);
Student s4 = new Student("3", "王五");
s4.setHeight(180);
TreeSet<Student> students = new TreeSet<>();
students.add(s1);
students.add(s2);
students.add(s4);
System.out.println(students);
}
}
会出错
上面的代码会报错,因为TreeSet不知道如何比较Student对象的大小。我们需要让Student类实现Comparable接口。
Step 3 实现Comparable接口
为了让TreeSet能够排序Student对象,我们需要在Student类中实现Comparable接口:
class Student implements Comparable<Student> {
String id;
String name;
int height; // 身高
public Student(String id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public void setHeight(int height) {
this.height = height;
}
public String toString() {
return id + ":" + name;
}
public int hashCode() {
return id.hashCode();
}
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj) {
return true;
}
if (!(obj instanceof Student)) {
return false;
}
Student other = (Student) obj;
return this.id.equals(other.id);
}
// 这个方法决定了排序规则
public int compareTo(Student other) {
if (this.height > other.height) {
return 1; // 返回正数:表示"我"比"你"大(我排在后面)
} else if (this.height < other.height) {
return -1; // 返回负数:表示"我"比"你"小(我排在前面)
} else {
return 0; // 返回0:表示"我"和"你"一样大
}
}
}import java.util.TreeSet;
public class Example12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student("1", "张三");
s1.setHeight(175);
Student s2 = new Student("2", "李四");
s2.setHeight(170);
Student s4 = new Student("3", "王五");
s4.setHeight(180);
TreeSet<Student> students = new TreeSet<>();
students.add(s1);
students.add(s2);
students.add(s4);
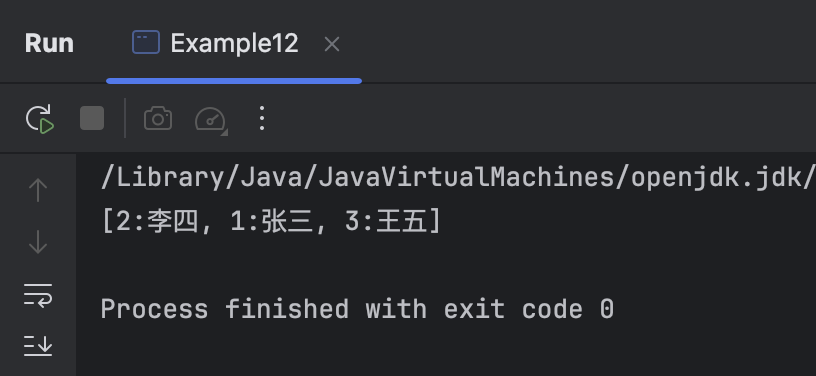
System.out.println(students);
}
}运行结果: